Aiming for factor4 of molding factories
Proposing foreign matter (contamination) countermeasures in molding by each process.
2022.10.20
In the plastic molding industry, contamination refers to foreign matter or dust that adheres to or mixes with molded products, and is often abbreviated as "contamination" in the field.
Foreign matter contamination in molded products = Contamination is likely to lead to complaints, requiring re-inspection of the product, and in some cases, resulting in the return of the product, causing great damage. In addition, it is difficult to pulverize and reuse molded products with contamination, leading to material waste.
Once contamination occurs, it takes a lot of time and money to return to a state where good products can be produced, and if there are many molding defects, it will lead to a loss of trust as a molding factory. Therefore, it is important to prevent contamination.
In this column, we will introduce contamination countermeasures in each process of molding with the contents of the following table of contents.
1. Conventional contamination countermeasures
2. Contamination criteria
3. Introduction of itinerary solutions
- Material receiver process
- Material transportation process
- Material drying process
- molding process
Summary
1. Conventional contamination countermeasures
One of the most frequently cited measures against contamination is the installation of a "clean room."
However, the installation and maintenance of a clean room is very costly. For example, a clean room for four molding machines of 100 to 200 tons is estimated to cost about 40 million yen. Properly maintaining a clean room not only costs money, but also takes a lot of effort.
In the first place, is it necessary to set up a large-scale clean room?
Setting up a clean room does not mean that all contamination can be prevented. The source of contamination is often outside the clean room. The important thing is to implement "appropriate measures" in "appropriate places".
2. Contamination criteria
As a premise, it can be said that foreign matter is mixed in or attached to all molded products. It is very difficult to completely eliminate contamination. Therefore, the "criteria for judging contamination" is important. Depending on the type, size (smallness), and degree of contamination (adhesion) of the foreign matter, it may not be a problem. In other words, it is important to understand the "criteria for judging contamination" for each molded product and to implement countermeasures that meet the required level.
Type of contamination
Then, what kind of things are mixed in molded products as foreign matter?
These are microscopic pictures of actual contamination.

At first glance, they all look like black spots, but they are actually made of different materials such as wood chips, stainless steel, and resin. In this way, foreign matter comes in a variety of materials, so if it is a piece of wood, the wooden pallet used on-site will be replaced with a plastic one, and if it is a piece of metal, a metal detector will be used. Preventive measures must be taken.
In addition, the types of foreign substances that must not be mixed in differ depending on the industry. For example, in the electronics industry, it is textile scraps and metal scraps, and in the medical equipment industry, it is textile scraps and skin flakes. Since the specifications required for each product are different, the types of contaminants that pose problems also differ.
Against this background, we can see that knowing the type of contamination is the first step in determining countermeasures.
Contamination size
The size of the foreign matter is also one of the important factors when considering countermeasures against contamination.
Smaller sizes may be acceptable. If it is OK if it cannot be confirmed with the naked eye, it is possible to install a filter that can remove 10 μm size particles.
*It is said that the size that the human eye can see is from 10 μm (0.01 mm).
Also, there may be cases where the metal powder you want to prevent contamination is 0.1 mm, but all the metal detectors you are considering can only remove metal up to 0.3 mm.
In such cases, it is necessary to switch to measures that "prevent the generation of metal powder in the first place."
When deciding countermeasures, it is necessary to confirm the standards for the allowable size of foreign matter.
In addition, the location where foreign matter adheres may be a problem. For example, foreign matter on the liquid crystal part, the part to be decorated, or the design surface is NG, but it is acceptable in other places.
For these reasons, it is important to understand the type and size of the foreign matter, compare it with the "contaminant judgment criteria", determine the method and level of foreign matter removal, and take countermeasures.
3. Introduction of itinerary solutions
After determining the types and sizes of foreign substances that need to be prevented from being mixed in, the next thing to consider is "how to prevent contamination." We will introduce specific examples of possible contamination countermeasures in the order of production line processes.
Material receiver process
Since the material Loading port is often used by people, it is a place where many foreign substances such as hair, skin fragments, and clothing fibers are generated. Garbage that has fallen on the floor or that is attached to material bags, etc., may enter. What kind of measures can be taken in the scene of material input?
Countermeasures against foreign matter contamination by automating raw material transfer
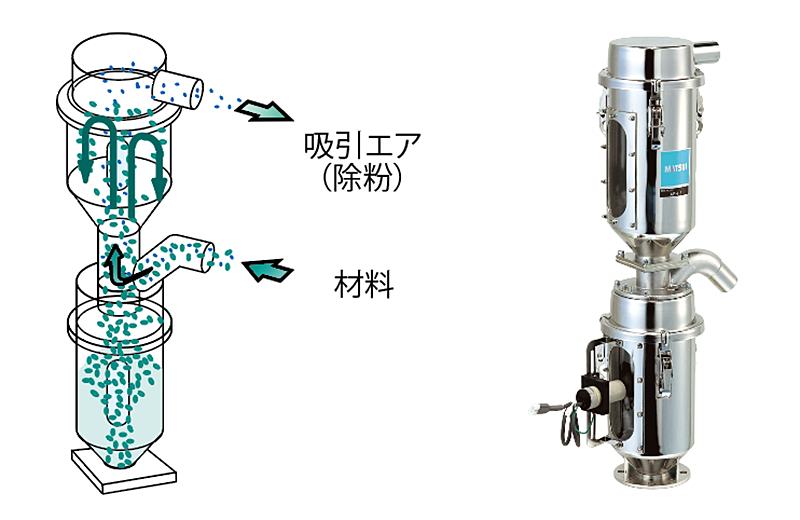
Many molding factory use flexible container bags (flexible containers). Flexible containers are convenient, but there is a possibility that dust adhering to the outside will get mixed in when the material is put into the tank by suspending it.
Possible countermeasures include wiping the flexible container and air blowing, but manual removal puts a heavy burden on workers and is also dangerous. Even if you remove it with an air blow, it is possible that the dust will rise up and fall into the tank. Therefore, we propose an automated device that suspends the flexible container and inserts the suction head into it.
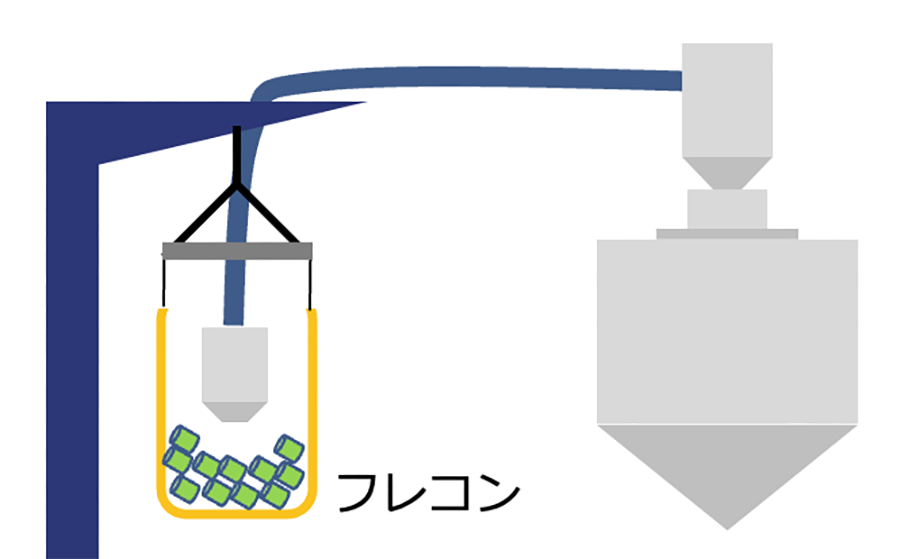
The FIBC itself is not lifted, eliminating the need to wipe the sides and bottom. All you have to do is remove the dust on the upper side, which improves work efficiency and safety. In addition, by hanging the four corners, the material can be brought to the center and transported, so there is very little leftover material.
Countermeasures against contamination of floating dust by creating a clean booth
Floating dust may enter the tank when materials are added.
Therefore, if it is difficult to create a clean room for the entire production line, we propose a solution that improves the cleanliness of only the space where materials are introduced.
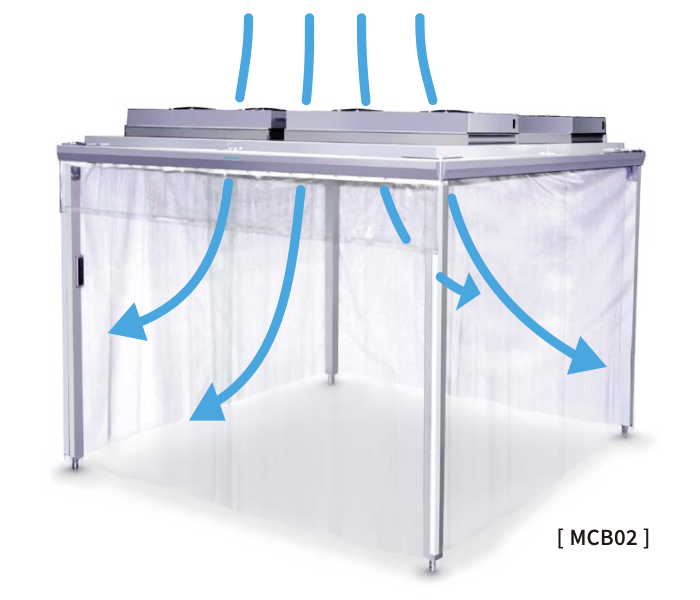

This is a method of making clean booths only in areas where you want to improve cleanliness.
A filter is installed on the ceiling surrounding the area, and a fan blows air from top to bottom to create a positive pressure in the space and create an air flow that expels dust to the outside. In addition, by eliminating static electricity inside the booth, it is possible to eliminate dust attached to material bags and workers. It is also possible to change the degree of cleanliness according to the application.
Powder removal measures before supply to the production process
Resin pellets rub against each other due to shaking during transportation and transportation, and resin powder is generated in the resin bag. In such cases, there is a method of separating pellets and powder before material feeding to control contamination.
A separator is installed between the material bag and the tank to separate pellets and resin powder. This allows clean pellets to be fed into the production line.
Material drying process
Contamination such as black spots is often a problem for products with strict hygiene and appearance standards. One of the causes of these black spots is carbonization and burning of the resin.
"Overdrying of resin" and "coldness of resin" are cited as causes of carbonization and burning of resin.
The resin is melted by the frictional heat that separates the pellets from each other as the screw of the molding machine rotates. This is called shear heating.
At this time, if the resin is too dry and no moisture remains inside, the generated shear heat tends to be too hot. This causes charring and burning. Resin also hardens as it cools, which also creates excessive resistance and causes high shear heating. In other words, in order to prevent black spots due to carbonization and burning, it is effective to suppress overdrying and cooling of the resin.
Measures against carbonization and burning (black spots) of resin by proper drying
The molding machine is repeatedly stopped for production planning, mold change, and trouble shooting, but isn't the dryer always in operation?
Also, if the amount of resin used decreases due to mold changes, the resin stays in the drying hopper for a long time. This causes the resin to become overdried, making it more susceptible to charring and burning.
On the other hand, it takes a lot of time and effort to stop the dryer at the same time as these small stops. There is also the risk of forgetting to start the system and stopping production, so it is not realistic to manage everything manually.
Therefore, it is effective to introduce a dryer with an appropriate drying function. This makes it possible to automate proper drying according to production.
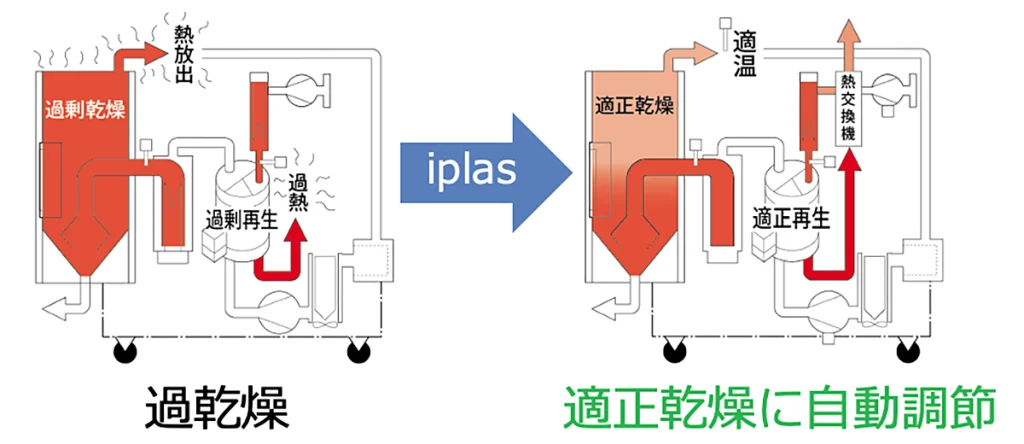
The dryer automatically reduces the heat load according to the operation status of the molding machine, thereby maintaining the proper drying condition of the resin. It can also be expected to have the effect of preventing yellowing of transparent molded products due to overdrying, and it will also lead to energy saving through proper operation.
For details, click here ⇒MJ6-i self-control Dehumidifying dryer
Material transportation process
Hose and piping material transportation routes have risks such as contamination due to damaged hoses, metal contamination caused by scraping of glass fibers in piping, and foreign objects entering through holes.
This time, I will introduce a specific example from a different perspective.
packing abrasion countermeasures by using ferrule piping for pipe connections
Pipes called IDF ferrules are generally used in production lines for optical and medical products. If the piping is not assembled correctly, the packing may protrude into the piping.
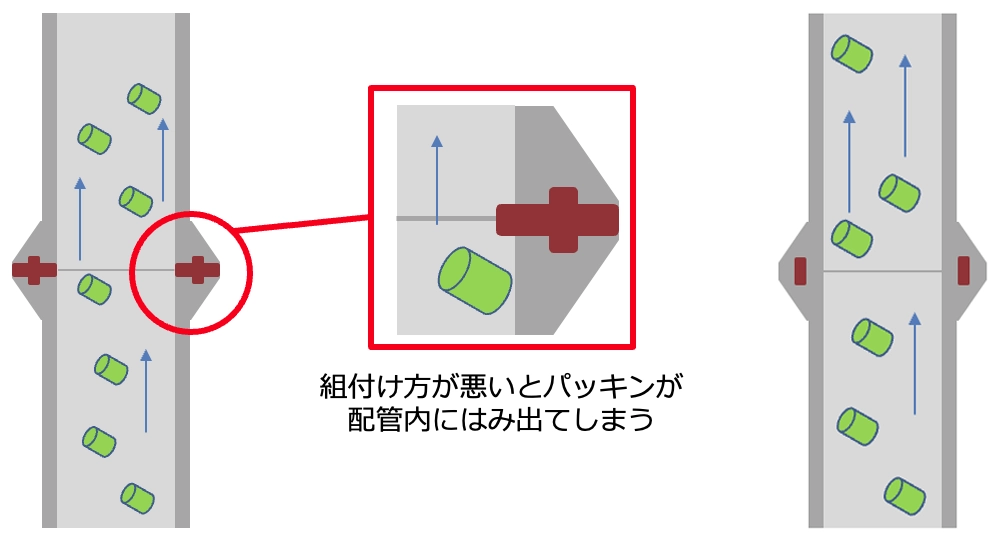
If the packing protrudes into the pipe, it will come into contact with the resin and be torn off, causing contamination.
In order to prevent this, it is effective to replace the ferrule with a structure in which the packing does not protrude. These ferrules are not affected by the quality of assembly.
Measures against material retention by reviewing piping and transportation methods
Constrictions may occur in the middle of Conveying hose, and resin may be retained at the rising parts of piping. This also causes variations in resin temperature and can cause charring and burning.

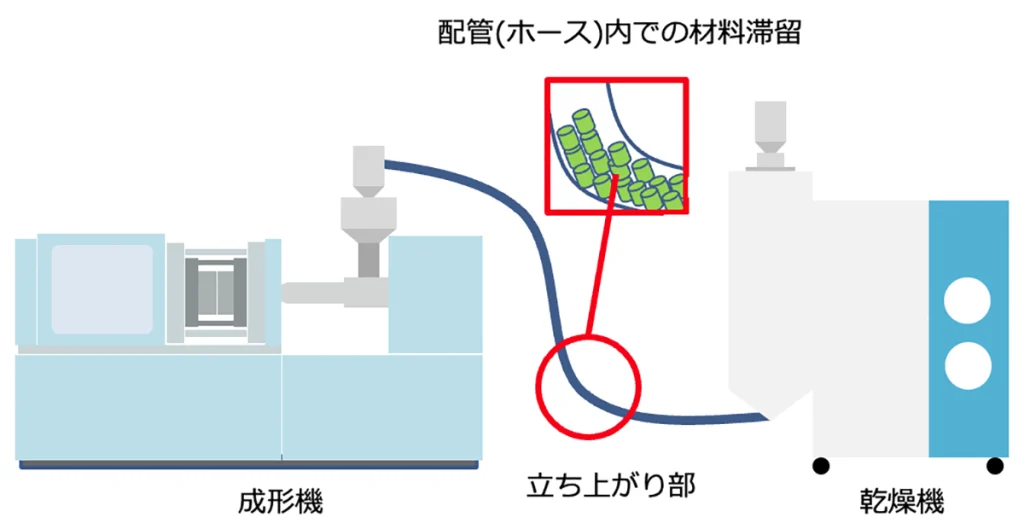
In order to prevent stagnation in the transportation route, it goes without saying that we use hoses that are not deformed, but if stagnation is occurring differences in the height of the piping or how it is routed, we can add a mechanism to feed the material completely. Is possible.
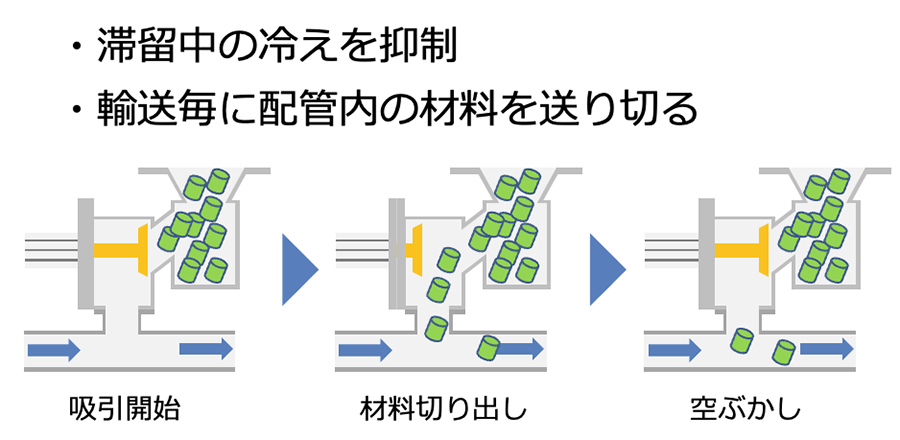

By supplying enough material to the piping while suction is applied, it eliminates stagnation in the transportation route. In addition, since there is no mechanism like a Slide gate, there is no generation of resin powder due to damper sliding.
Measures to remove resin powder generated during transportation
Resin powder may be generated not only inside the material bag but also inside the piping.
When pellets collide with bends in pipes, they crack and generate resin powder.
There are several workarounds for this.
If the resin powder does not adhere to the pellets, "centrifugation" is effective. ⇒ ARV

By attaching it to a transportation line such as a dryer, it is possible to remove resin powder from the pipe.
If the resin powder adheres to the pellet, there is a method called "air mixing".
By attaching an "airflow mixing collector", the resin particles are hit against each other and the resin powder is separated from the pellets. Resin dust is removed by suction, resulting in a clean pellet delivery.
Click here for details ⇒ Aero Power Hopper (Filterless Type) APH
There is also a method to remove the resin powder by the "static elimination function".
Since the resin powder adheres to the pellets due to static electricity, the powder is separated from the pellets by blowing static-removing air, and the powder is collected into the waste tube by the flow of air.
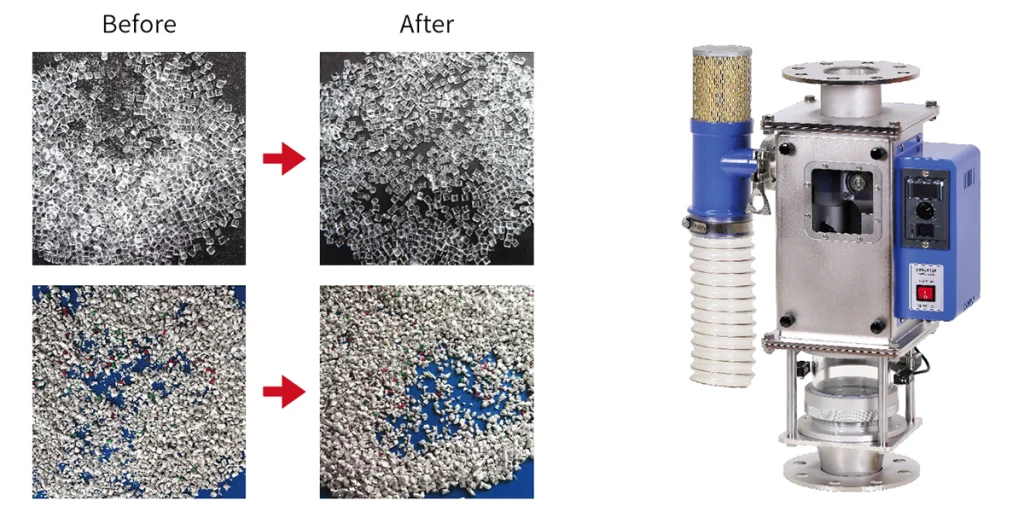

It can be used according to the amount of resin used because it can process more than the "airflow mixing collector".
molding process
Even if you take care not to mix foreign matter into the material, foreign matter may adhere to the molded product. Foreign matter adhering to the surface of a molded product can cause coating defects on parts to be painted, and can cause electricity to flow in electronic parts.
What kind of countermeasures should be taken to solve the problem of dust floating around the molding machine adhering to products due to static electricity?
Countermeasures against adhesion of floating dust to molded products by neutralizing static electricity
As a general countermeasure against static electricity, it is static elimination blow with an ionizer. However, if the static elimination air does not hit the parts, there is no static elimination effect, and there is a risk that the mold temperature will drop by blowing the air. Lowering the mold temperature may cause molding defects.
Therefore, the electric line of force radiation method is effective. This is a method of intensively removing static electricity from the mold opening space using electric lines of force.
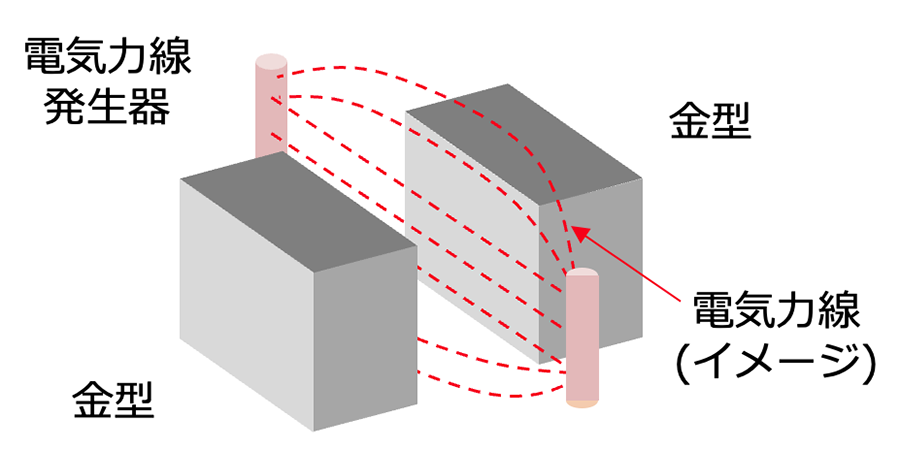
By attaching a positive electrode and a negative electrode to both sides of the mold, electric lines of force are formed to eliminate static electricity. There is no risk of the mold temperature dropping because it can be dealt with in no wind.
Reduction of charged voltage by humidification (humidity control)
Humidification is effective when you want to eliminate static electricity in a wider space.
Humidification lowers the charged voltage and at the same time allows floating debris to settle.
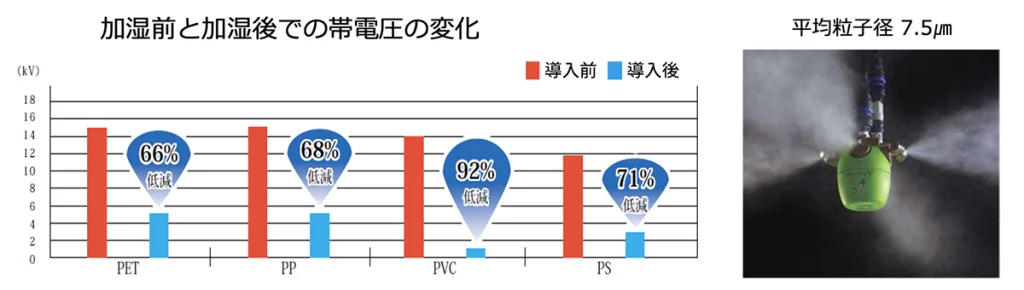
It is well known that humidification is an effective countermeasure against static electricity. , can eliminate static electricity over a wide area while preventing equipment from getting wet.
Summary
Standards for contamination in molded products differ depending on the industry and product, and the causes of contamination also vary depending on the molding environment. It is important to understand the criteria for contamination, identify the location and cause of contamination, and take appropriate countermeasures.
At MATSUI, based on the concept of factor 4, "factor4 wealth, half resource consumption", we will actively propose environmentally friendly molding factory and eventually improve resource productivity. Please feel free to contact us if you have any problems.
Sales Engineering Department Yuki Yagi