持続可能な成形工場へー環境と経営を両立する時代
環境対応が企業価値を高める時代へ
近年、カーボンニュートラルの実現に向けた取り組みは、生産業界全体で加速しています。日本の温室効果ガス(GHG)排出量のうち、中小企業が占める割合は1~2割にのぼり、その削減は欠かせない課題です。加えて、グローバルに展開する大企業の多くが、国際的な目標である「1.5℃水準」に整合した削減目標(SBT)を掲げ、サプライチェーン全体に排出削減を求める流れが進んでいます。そのため、取引先である中小企業にも、温室効果ガス削減への取り組みやその実績が強く求められるようになっています。
さらに金融機関では、環境配慮に積極的な企業を支援する動きが広がっており、削減活動は資金調達や新規取引の拡大につながります。つまり、脱炭素化は社会的責任であると同時に、経営上の大きなメリットを生む取り組みなのです。
環境省:温室効果ガス排出削減等指針に沿った取組のすすめ~中小事業者版~
カーボンニュートラル実現には、脱炭素への取り組みが欠かせません。近年、その重要性への関心が高まっており、実際に取り組みを進める企業や組織の割合も年々増加しています。
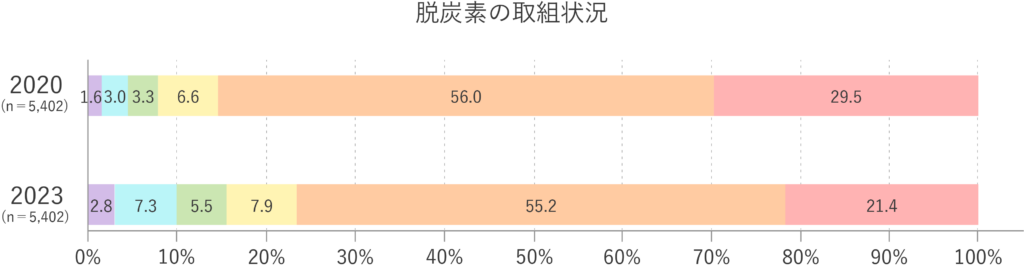
経済産業省 中小企業庁:2024年版 中小企業白書(第1部第4章第5節)
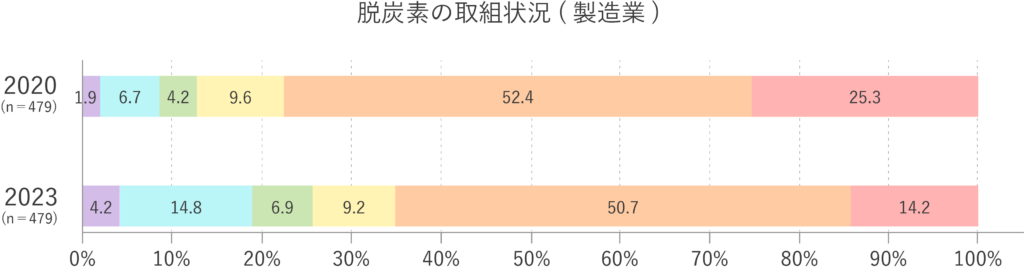
経済産業省 中小企業庁:2024年版 中小企業白書(第1部第4章第5節)

環境対応とコスト削減、両立の必然性
世界的なエネルギー価格高騰を背景に、近年、日本でも電気料金の上昇が顕著になっています。
このような電気料金の高騰は、プラスチック成形工場にとって非常に深刻な課題です。成形機をはじめとする設備の稼働には大量の電力が必要であり、その消費はランニングコストに大きく直結します。特にヒーター加熱を中心とした熱源系の動作は、電力消費が非常に大きく、電気料金高騰下では工場の採算に直接的な影響を及ぼします。成形工場では、24時間稼働や多台数運転であるため、電気代の高騰によるコスト増は、利益率の圧迫や価格競争力の低下につながります。特に低単価大量生産の製品では、電気代が原価に占める割合が大きく、対応策なくしては経営面のリスクが高まります。
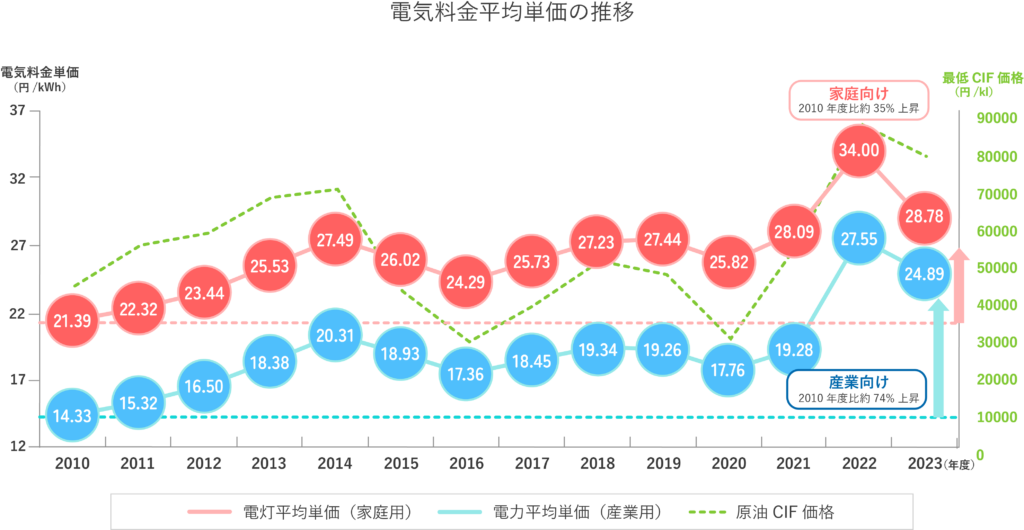
経済産業省 資源エネルギー庁:日本のエネルギー2024年度版「エネルギーの今を知る10の質問」3.経済性
一方で、カーボンニュートラルの実現に向け、エネルギーの効率化やCO2排出削減も同時に求められています。つまり、成形工場は「環境対応」と「コスト削減」という二重のプレッシャーにさらされているのです。
だからこそ今、現場には「省エネルギーとコスト削減を両立させる仕組み」が欠かせません。電気料金の上昇を逆手に取り、効率化や設備改善を進めることは、コスト競争力の強化だけでなく、持続可能な工場運営への一歩にもつながります。

環境対応と省エネの両方を適える対策は、成形現場においても、身近なところで導入されています。
成形現場を蝕む「熱」の影響
熱対策の定番とされる断熱板
金型温度調節機は、金型を所定の温度に保つために欠かせない装置です。しかし、その熱は金型だけでなく成形機本体にまで伝わってしまうことをご存じでしょうか。金型から伝わる熱により、成形機全体が「延びる」現象を引き起こし、型締力の低下や成形精度への影響を招きます。
※成形機に搭載されている「自動型圧調整」機能は、この延びによる型締力の低下を補うための仕組みです。
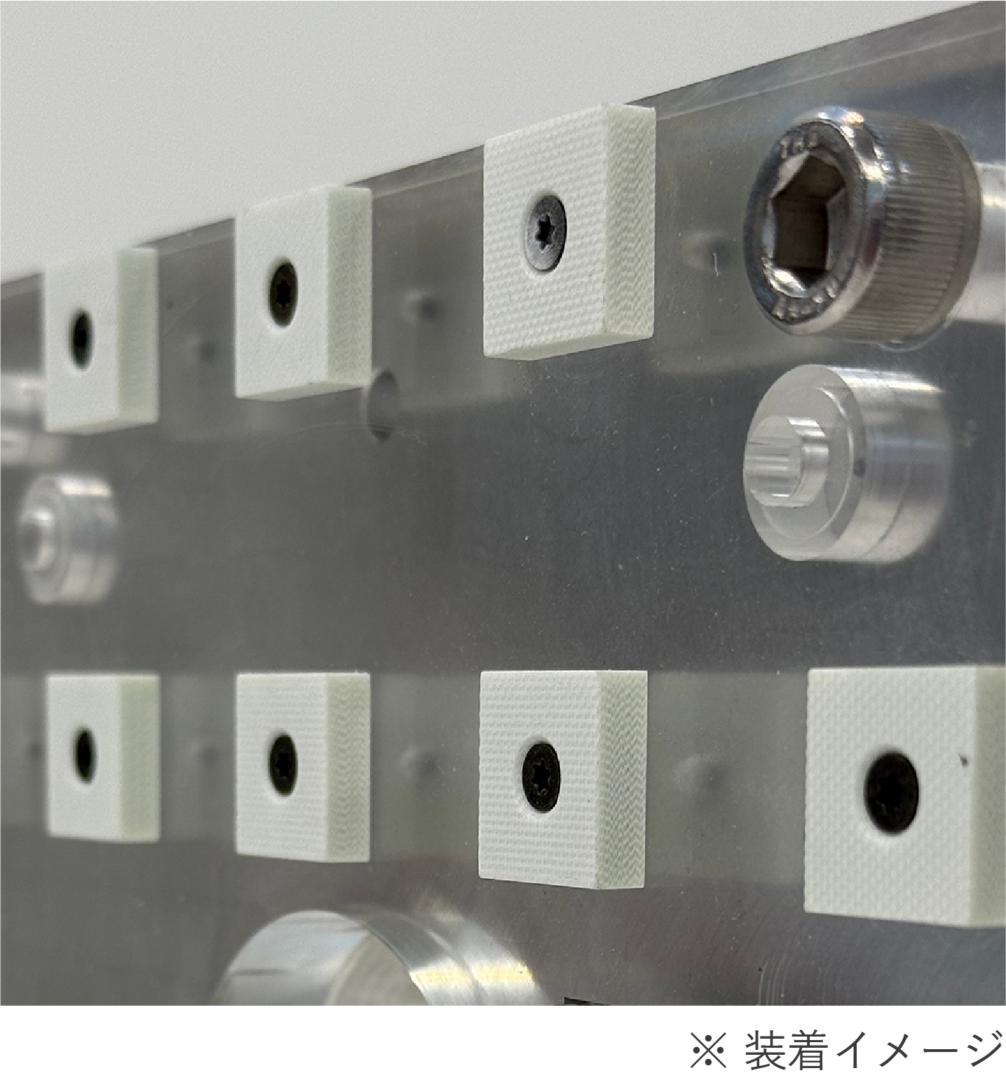
そこで多くの現場では、身近な対策として「断熱板」が用いられています。プラテンと金型の間に挟むことで、直接的な熱の伝導を抑える働きが期待できるためです。ところが、断熱効果は素材によって差があり、また装着用に設けられたボルト穴を通じてプラテンと成形機が広く接触するため、そこから熱が伝わってしまいます。つまり、断熱板は有効な手立てではあるものの、決して十分とは言えません。
断熱板では防ぎきれない熱の伝わり方
断熱板が遮断できるのは、あくまで金型とプラテンの接触面における熱伝導です。しかし、実際には取付けボルトやロケートリングといった部分を通じても熱は伝わり、そこから成形機全体に広がっていきます。これら複数のルートを遮断しなければ、ムダな放熱を防ぐことはできないのです。
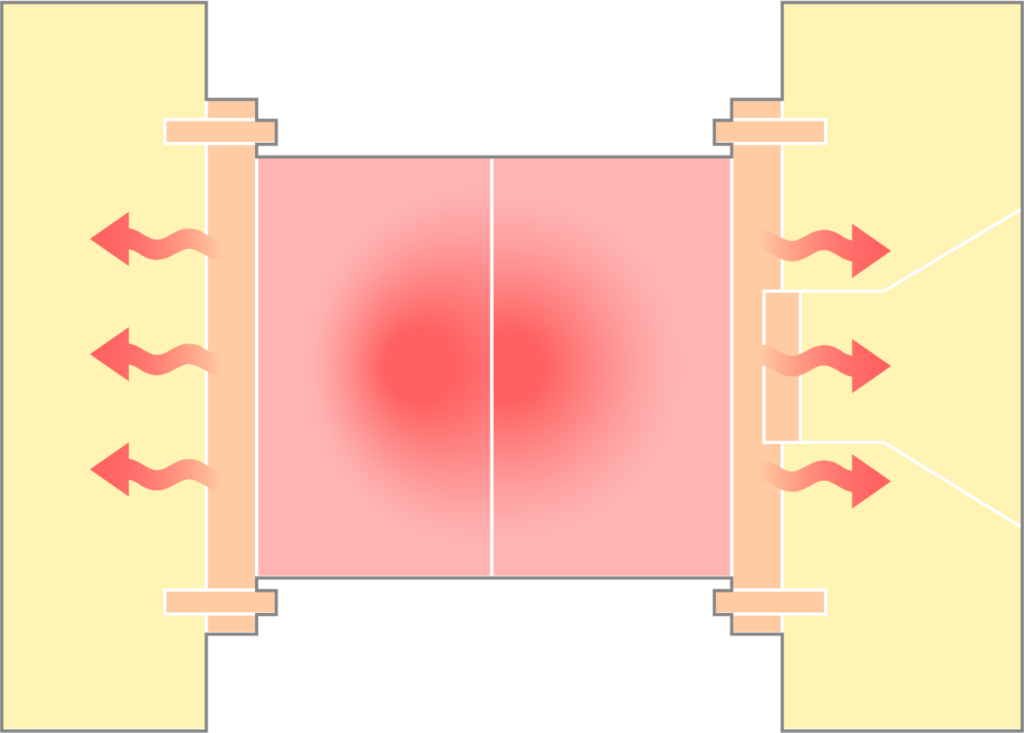
① 金型取付け板から
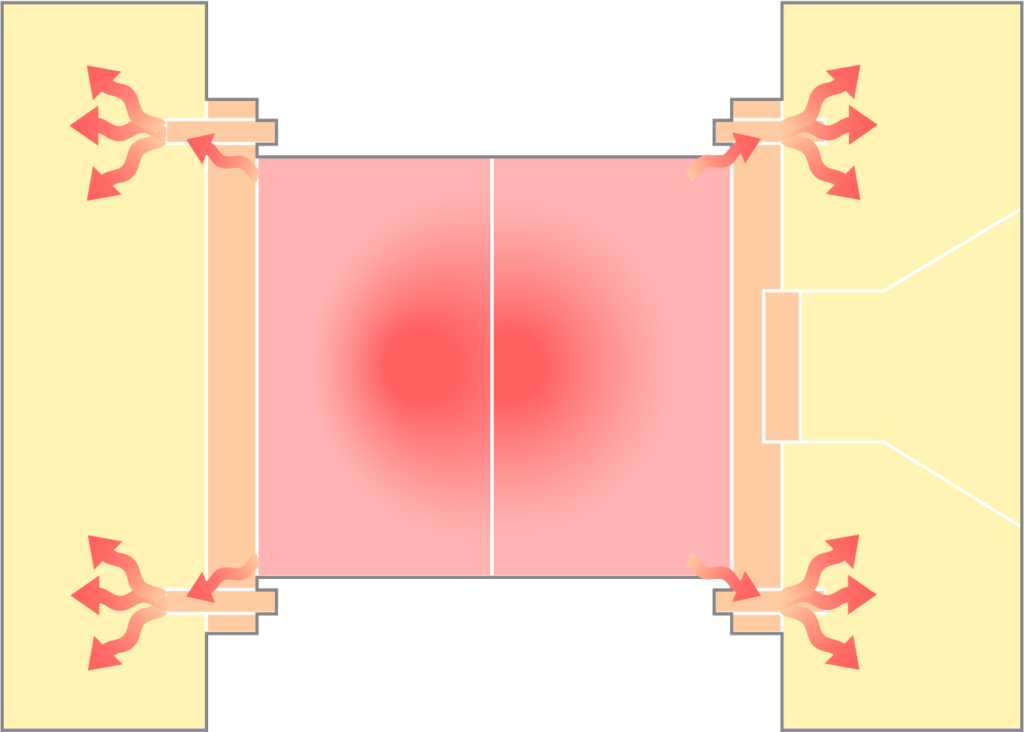
② 取付けボルトから
③ ロケートリングから

成形機に熱が伝わると、鉄がわずかに膨張し、ミクロン単位で「延びる」現象が起こります。その結果、型締めバランスが崩れ、製品寸法や品質に影響を与えてしまいます。
3方向から遮断し、成形機を熱から守る
効果的な断熱対策として提案するのがTamaGONです。
TamaGONはプラテンと金型の間に「空気断熱層」を作り、金型からプラテンへ伝わる熱の移行を大幅に抑制します。
熱の伝わりやすさは、一般的に以下の計算で決まります。

TamaGONは、プラテンとの接触面積を減らし、空気による断熱層を形成することで、伝導率を小さくします。
1.金型取付け板からの熱を遮断
金型を加熱すると、その熱は金型取付け板を介してプラテンにも伝わります。
TamaGONはプラテンと金型の間に空気層を設けることで、取付け板からプラテンへの熱移行を大幅に削減します。これにより、プラテンの不要な温度上昇を抑え、成形機全体の寸法安定性や成形品の品質安定にもつながります。

① 金型取付け板から
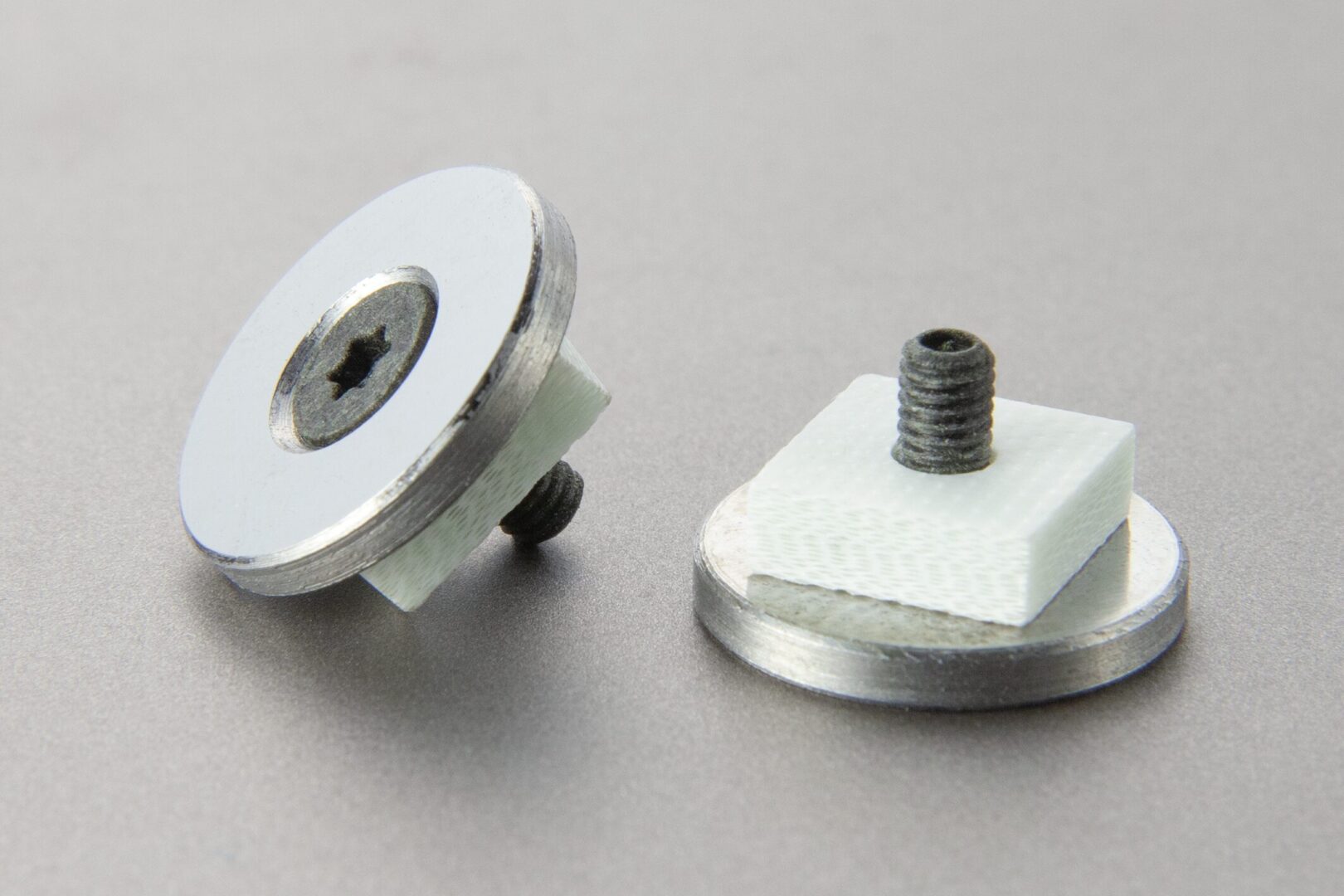
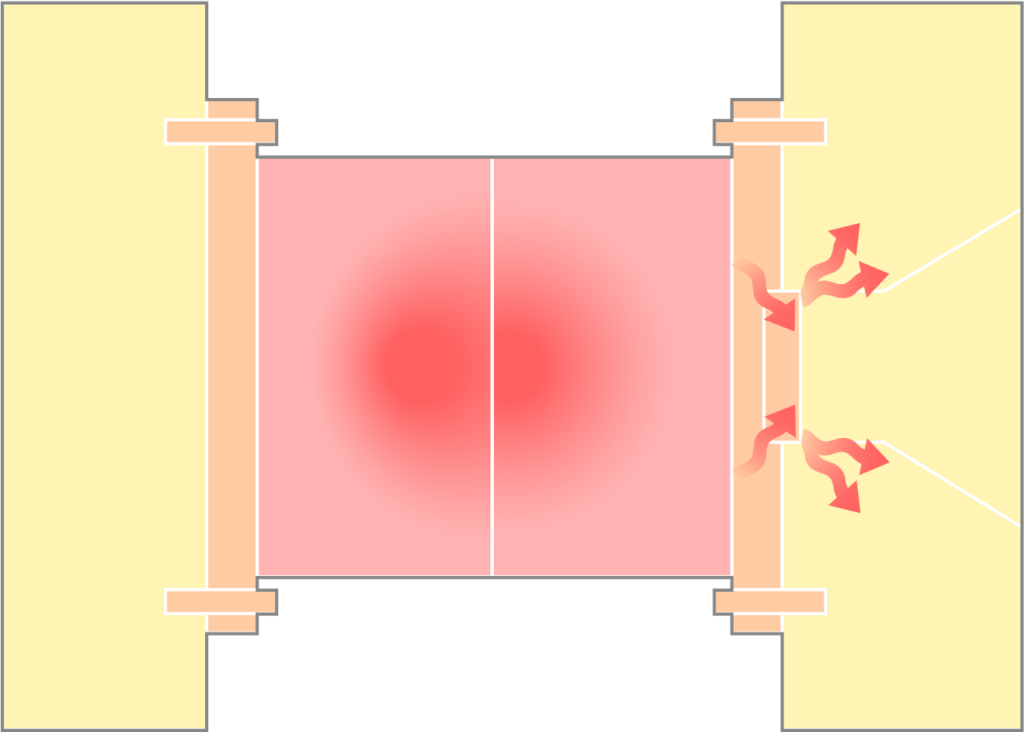
2.取付けボルトからの熱を遮断
成形現場では、金型とプラテンを強固に締結するための取付けボルトが不可欠です。しかし、金属製のボルトは熱を通しやすく、金型の熱がダイレクトにプラテンへ伝わる熱の通り道となってしまいます。
そこで、TamaGONを、エアクランプや断熱ワッシャと組み合わせて設置。これにより、ボルト経由の熱移行を大幅に抑え、プラテンの局部的な温度上昇を防ぎます。

② 取付けボルトから
3.ロケートリングからの熱を遮断
ロケートリングは金型位置を決める重要な部品ですが、その肉厚部分は熱の供給源にもなります。通常のロケートリングはプラテンと密着し、そこから効率的に熱が伝わってしまいます。
そのため、肉厚部を肉抜きする特殊設計を採用。熱伝導経路を遮断し、ロケートリングからプラテンへの熱移行を最小化します。

③ ロケートリングから

エアクランプと断熱ワッシャをTamaGONと組み合わせることで、ボトルから伝わる熱の断熱対策をすることができるんですね。

その通りです。TamaGONと併用することで、局所的な温度上昇を防ぎ、安定した成形環境を維持することが可能です。
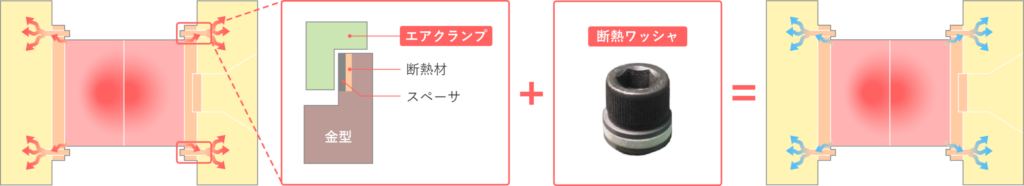

なるほど…。では、ロケートリングの形状は具体的にどう違うんですか?

こちらをご覧ください。肉厚部に肉抜きを施した形状になっており、従来型に比べてプラテンへの熱移行を最小限に抑えられます。

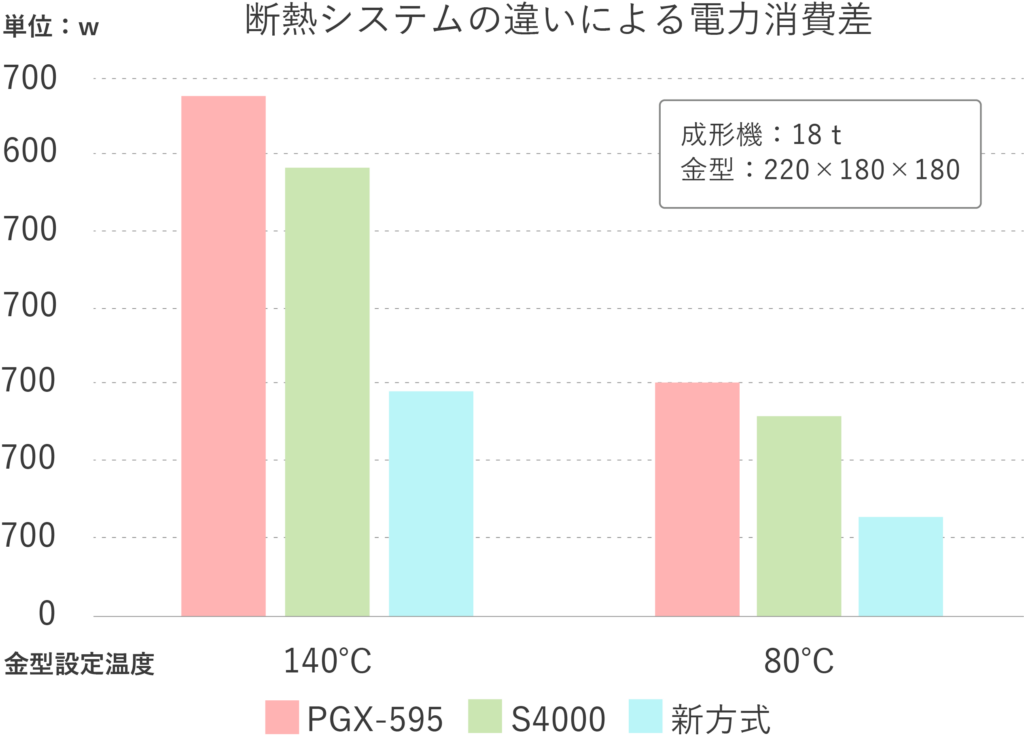
効果事例
通常の断熱板の場合と、3つの伝熱ルートに対策を施した「TamaGON+α(エアクランプ、断熱ワッシャ、特殊ロケートリング)」を比較したところ、最大で約60%の電力消費効果が確認できました。さらに、省エネだけでなく、金型の昇温時間を短縮できるほか、必要なヒーター容量が小さくなるため、温調機の小型化といったメリットも得られます。