A molding process that beautifies both the appearance and the earth
As the common theme across the industry is to achieve both high-quality appearance and environmental friendliness, heat and cool molding is attracting attention. In fields such as automobiles, home appliances, and medical equipment, where appearance quality is directly linked to brand value and reliability, the finish of the molding surface determines competitiveness.
In the medical field, even the slightest weld line can affect strength, airtightness, and transparency, threatening the safety and reliability of precision equipment. In particular, for disposable products and diagnostic cartridges, even minute defects can lead to fatal problems, so a process that uses high-temperature molding and rapid cooling technology to melt and fuse resin uniformly is essential for quality assurance.
Meanwhile, in the fields of automobiles and home appliances, the trend toward "paintless" products, which can achieve mirror-like or piano-black finishes without relying on paint, is accelerating. Eliminating the painting process not only reduces costs, but is also attracting attention as a way to comply with VOC emission regulations and carbon neutrality.
Heat & Cool molding is a technology that solves these two issues of "quality" and "environment" in one process.
What is Heat & Cool Molding?
Molding technology that dynamically controls mold temperature to achieve both high-level appearance and functionality
Heat & Cool molding, also known as weldless molding, is a molding method in which the mold temperature is rapidly heated to the resin softening point during one molding cycle, and then rapidly cooled to a temperature at which the part can be removed, improving mold transferability and achieving surface quality not achievable with general molding. The surface quality that can be expected to be achieved includes improved weld lines, surface gloss, and reduced warpage and sink marks.
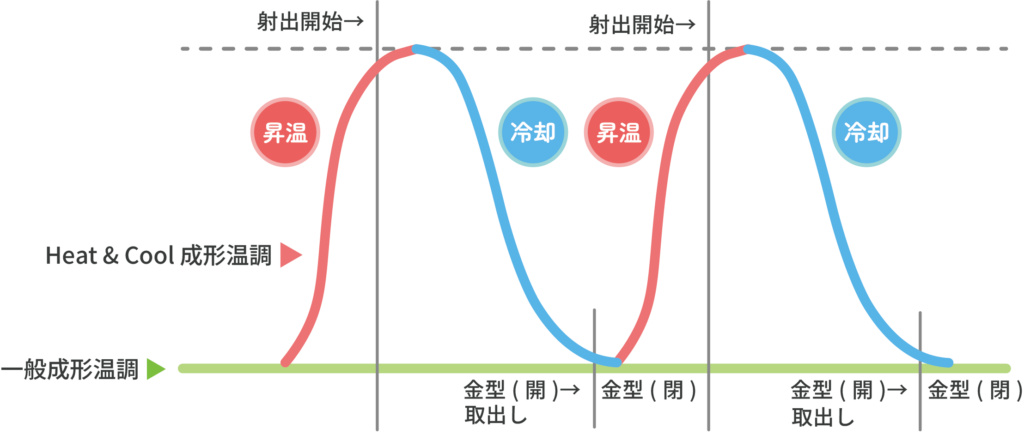
In heat and cool molding, mold temperature is regulated by repeatedly increasing and decreasing the temperature.
[Purpose of each process]
Heat: Rapidly heat the mold surface temperature to increase the fluidity of the molten resin inside the mold.
Cool: Rapidly cools the mold surface temperature, maintaining the shape of the molded product.
Rapid cooling reduces the cooling time, and uniform cooling reduces deformation after molding, leading to Improve Dimensional Precision.
*Linear scratches that occur when the leading edges of resin flow collide. Weld lines are a defect in appearance products, and are also a defect in functional parts because they cause a lack of strength. Welds occur when a molded product has an opening or is injected through a multi-point gate.
Heat & Cool Solutions
1. Improvement of weld lines
Heating the mold to a high temperature increases the resin fluidity, which in turn improves adhesion between the flow ends of the molten resin compared to regular molding, making it possible to reduce weld lines to a level that is no longer visible to the naked eye *.
Weld lines appear at the resin joint
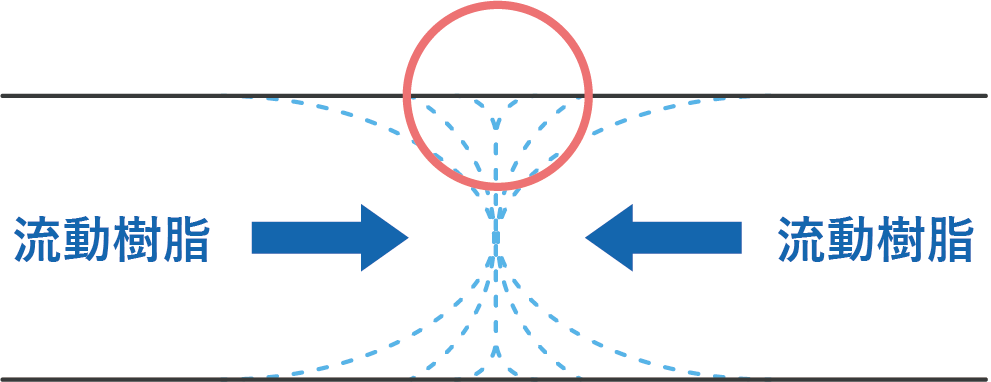
Mold Sectional view
Improved adhesion between dissolved resins
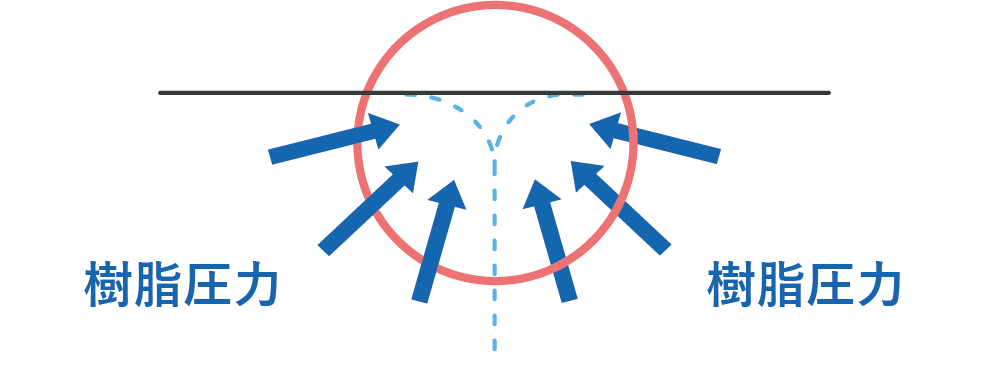
Enlarged view of weld area
*The physical action of resins colliding with each other remains unchanged. It improves the adhesion of the resin fused area and makes the weld invisible.
2. Improvement of poor transfer
Heating reduces the viscosity of the molten resin in the mold and improves its fluidity, allowing the resin to reach every detail of the mold's molding surface, improving transfer defects. Therefore, it is possible to achieve matte molding with texture transfer and glossy molding with mirror transfer with Heat & Cool molding.
[Improvement of poor grain transfer]
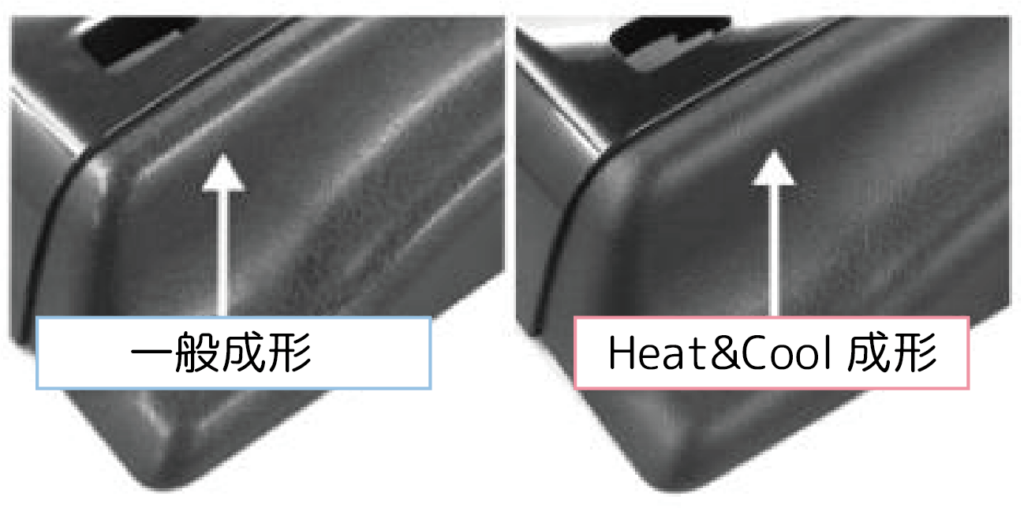
[Improvement of mirror surface transfer defects]
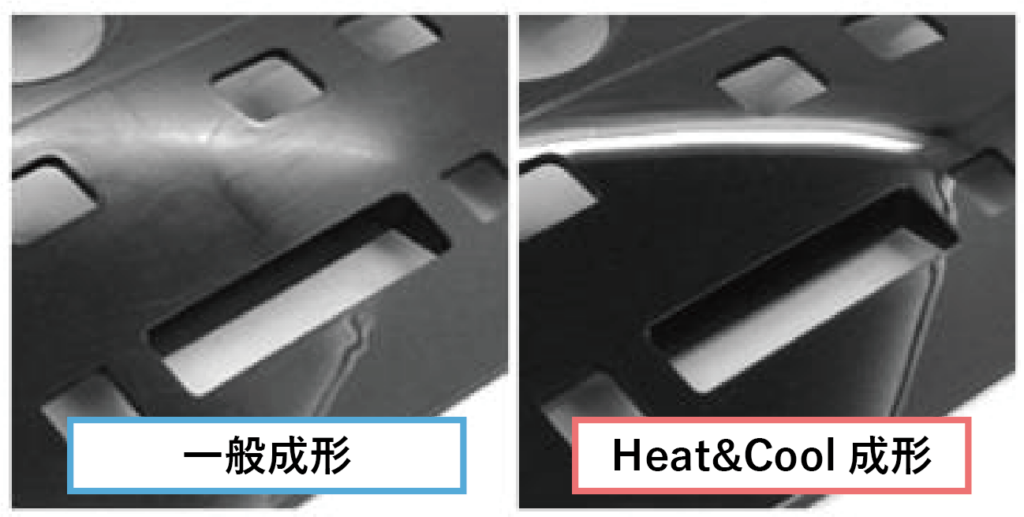
3. Improved filler exposure
Filler exposure refers to additives such as glass fibers that are mixed into resin to give it strength, heat-resistant resistance, and various other resistance properties, being visible on the surface of the molded product. Heat & Cool molding can suppress the exposure of glass fibers and achieve good surface quality.
[Mechanism of expression]
In general molding, the movement of the fountain flow causes the filler to fly outward from the flow front, where it solidifies while pressed against the mold wall, leaving the filler visible on the surface.
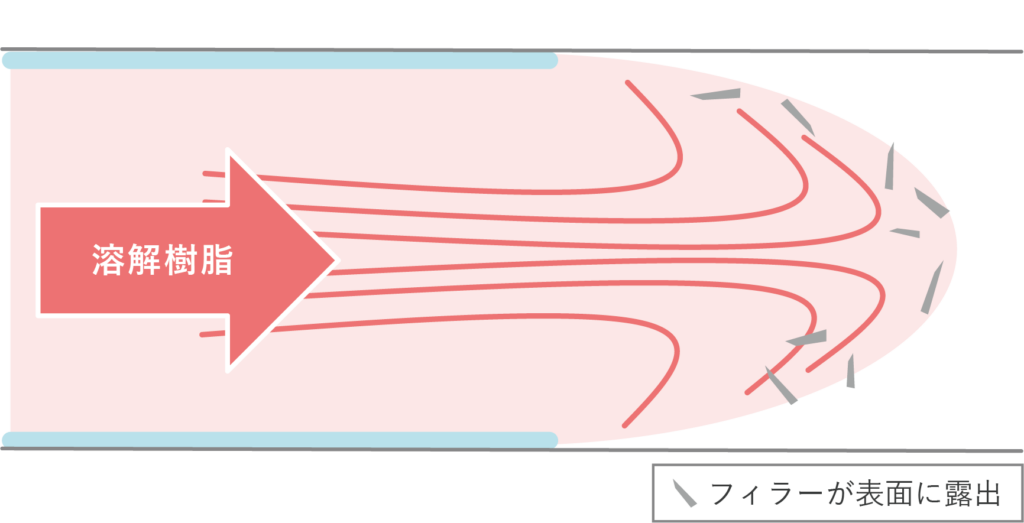
Skin layer
The molten resin cools from the point where it comes into contact with the mold surface, solidifying instantly and becoming a film-like substance.
Fountain Flow
A flow pattern in which resin springs from the center due to the skin layer and flows like a fountain on both sides of the wall.
➡ The resin ejected into the mold cools at the point where it comes into contact with the mold surface, causing it to lose fluidity.
Flow Front
The tip of the resin flowing into the mold.
[Improvement mechanism]
Because the temperature of the mold wall is high, the molten resin around the pressed filler is kept warm, and during this time the molten resin covers the filler due to the mold pressure, making it possible to prevent the filler from exposing.
[General molding]
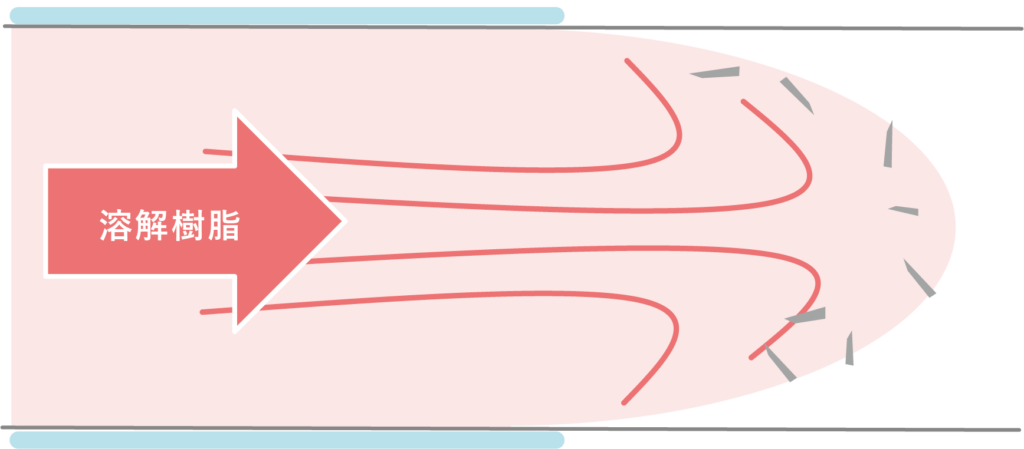
[Heat&Cool molding]
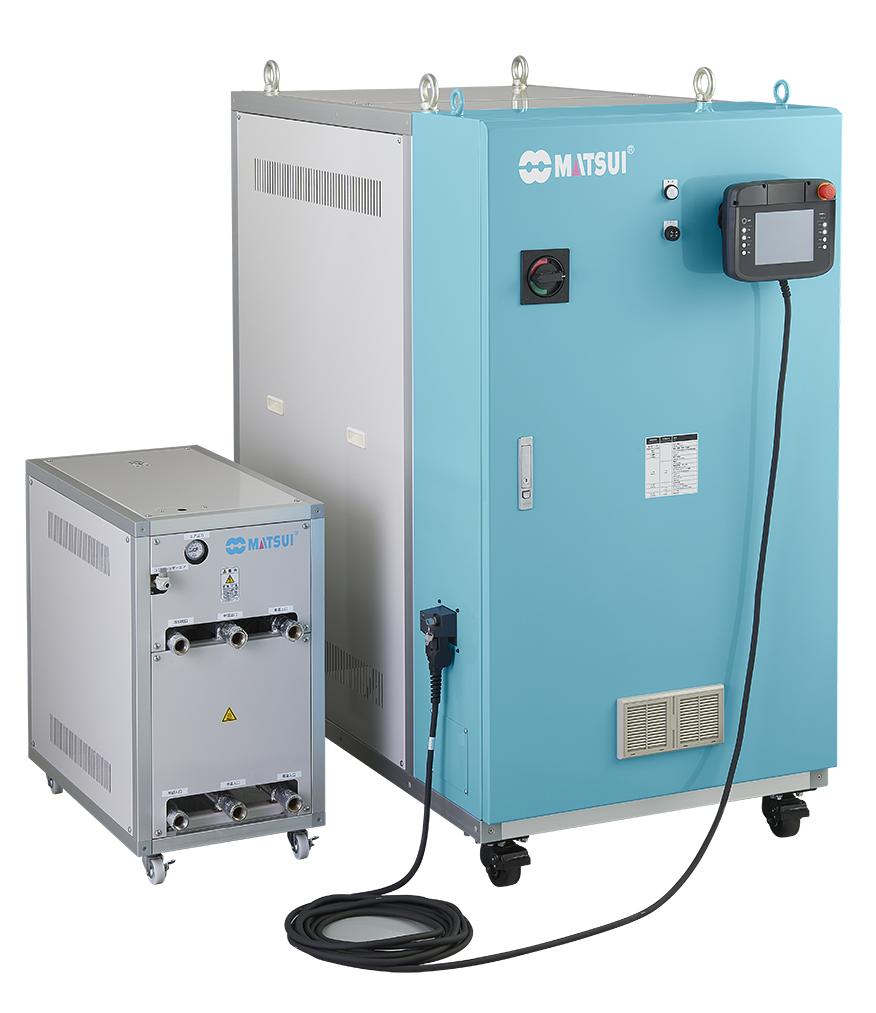
Heat & Cool molding lineup
Three types of lineup and characteristics
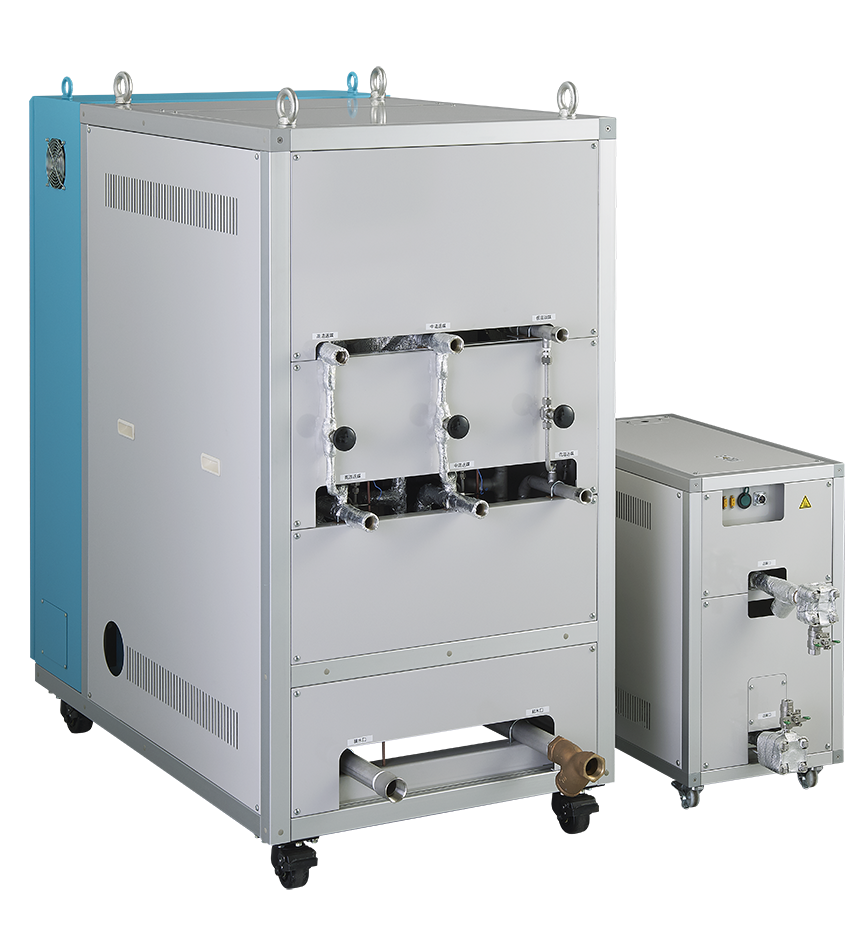
We will introduce three types of Heat & Cool molding. The three most common types are "compressed hot water type," "steam type," and "oil medium type," and we will introduce the temperature reached, equipment configuration, and features of each method.
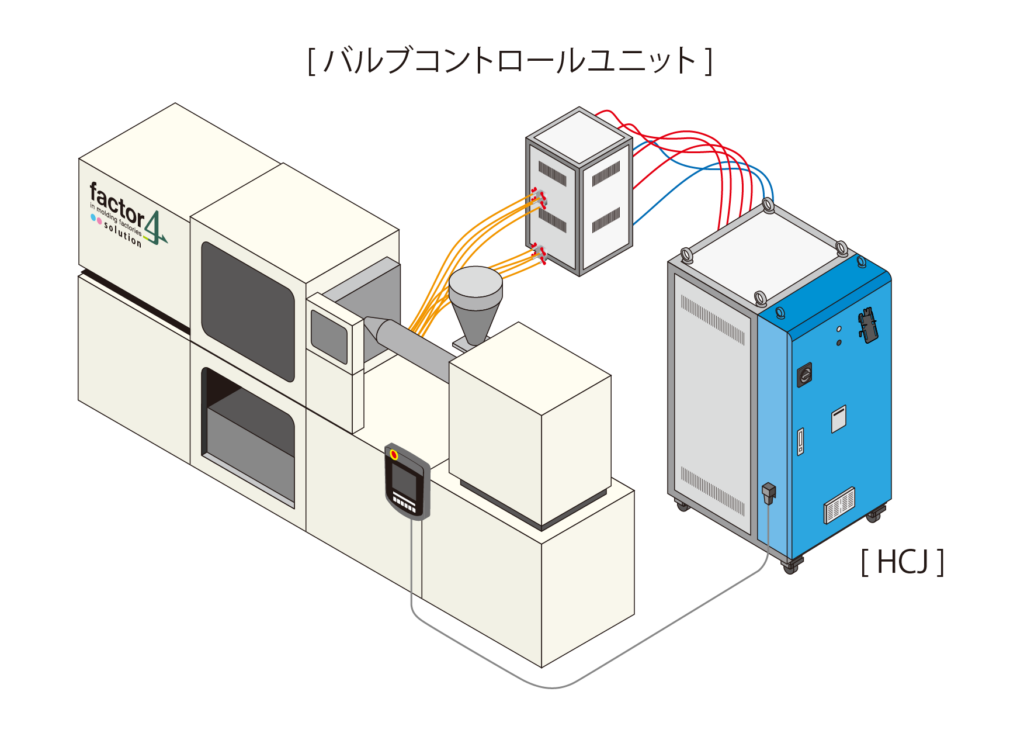
pressurized hot water
A method of heating and cooling by switching between pressurized hot water and cooling water
Medium temperature (water): max. 200℃
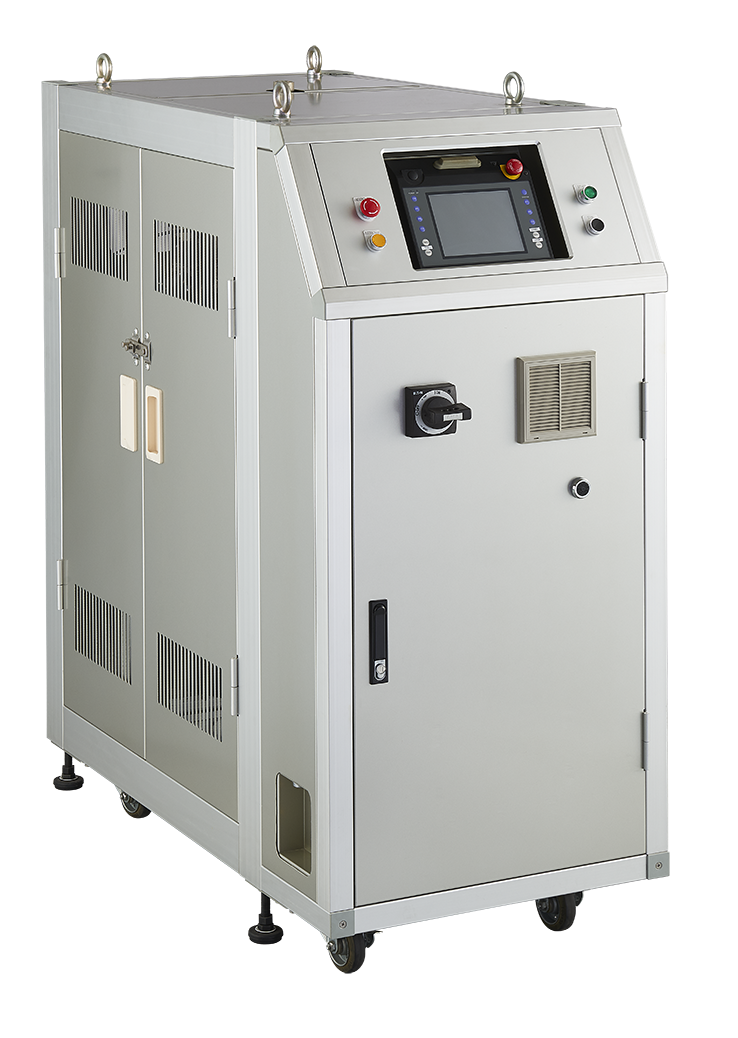
Equipment configuration: HCJ or Mold Temperature Controller x 3 / valve unit
Feature 1: Equipment costs are lower than steam systems
Feature 2: No boiler required
steam type
A method of heating and cooling by switching between steam and cooling water
Medium temperature (steam): Maximum 180°C
Medium temperature (water): 35℃ or less
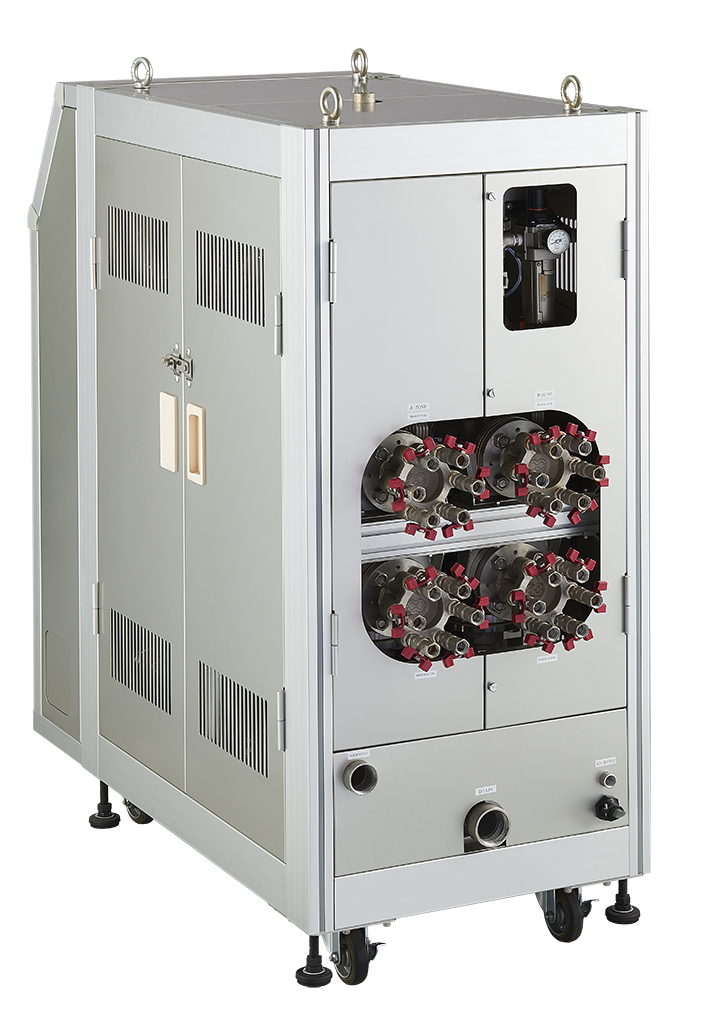
Equipment configuration: RHCM / Mold Temperature Controller / boiler (simple type, electric ◎) / cooling tower
Feature 1: Steam has high thermal conductivity, allowing for rapid temperature rise 2.5 to 6 times faster than hot water heating.
Feature 2: By using a special mold, the temperature of the mold surface can be controlled uniformly in a short time.
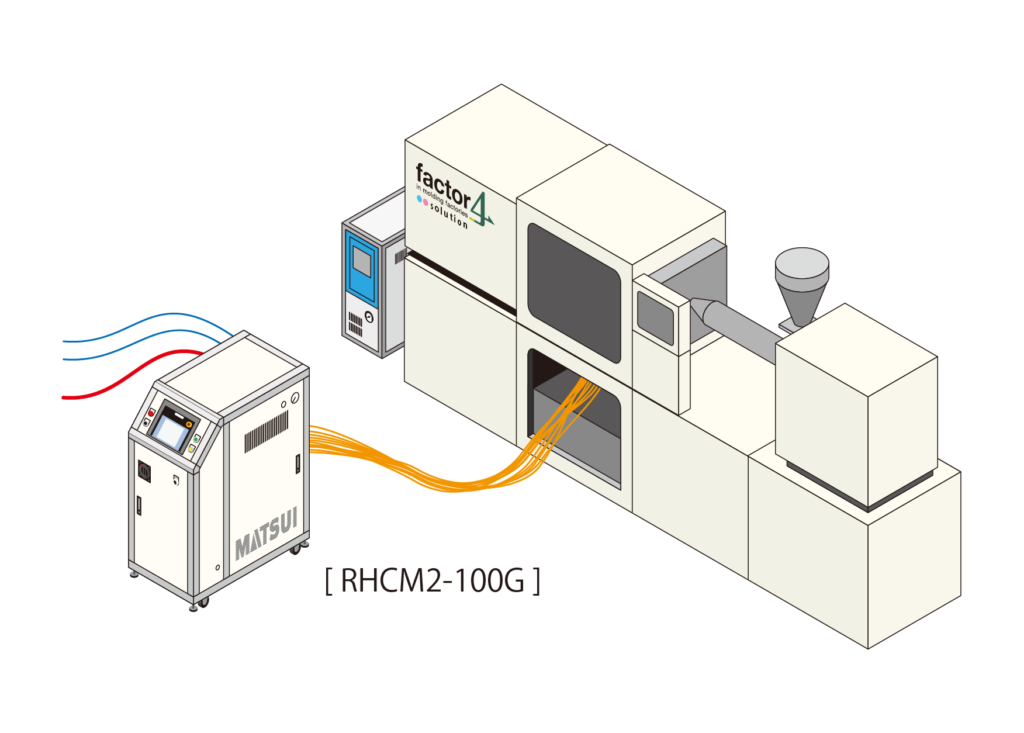

The boilers are simple, so no license is required. In addition to fuel-fired boilers, electric boilers are also available. We provide total support, from equipment selection to installation and start-up.
oil medium type
Heating and cooling are performed by switching between heating oil and cooling oil.
Medium temperature (oil): 40~300℃
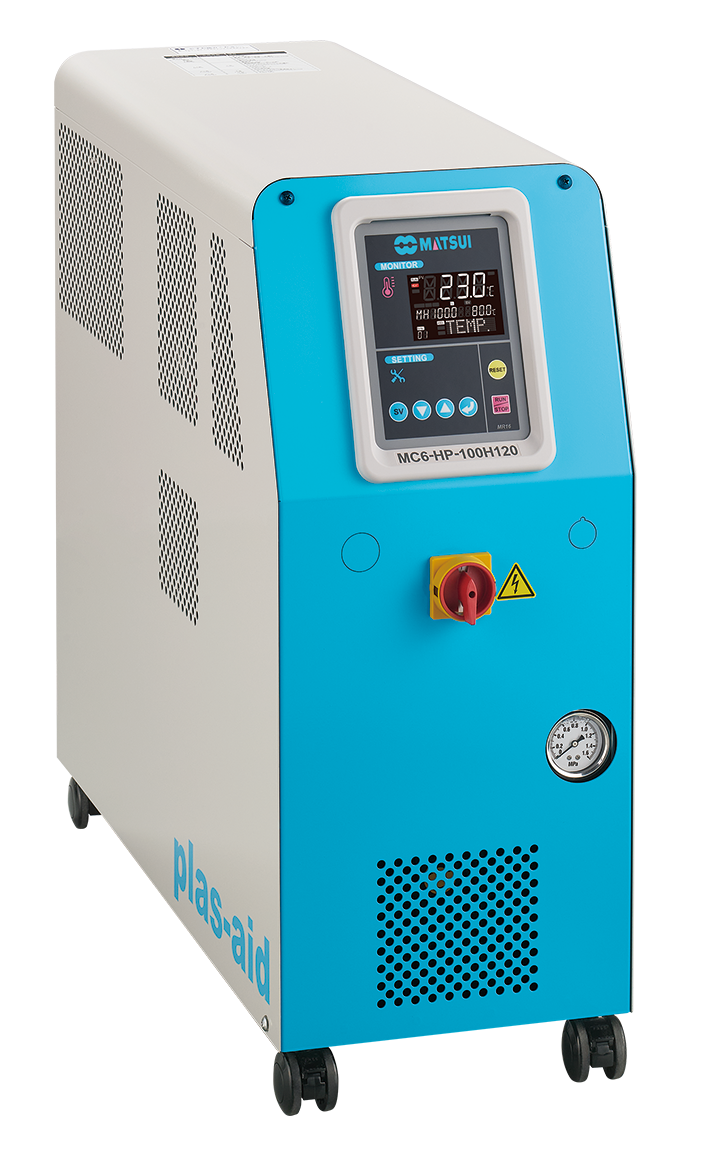
Equipment configuration: Oil medium Mold Temperature Controller
Feature 1: Suitable for functional parts and thick structural parts made of high heat-resistant resin.
Feature 2: By using a special mold, more uniform temperature control is possible.
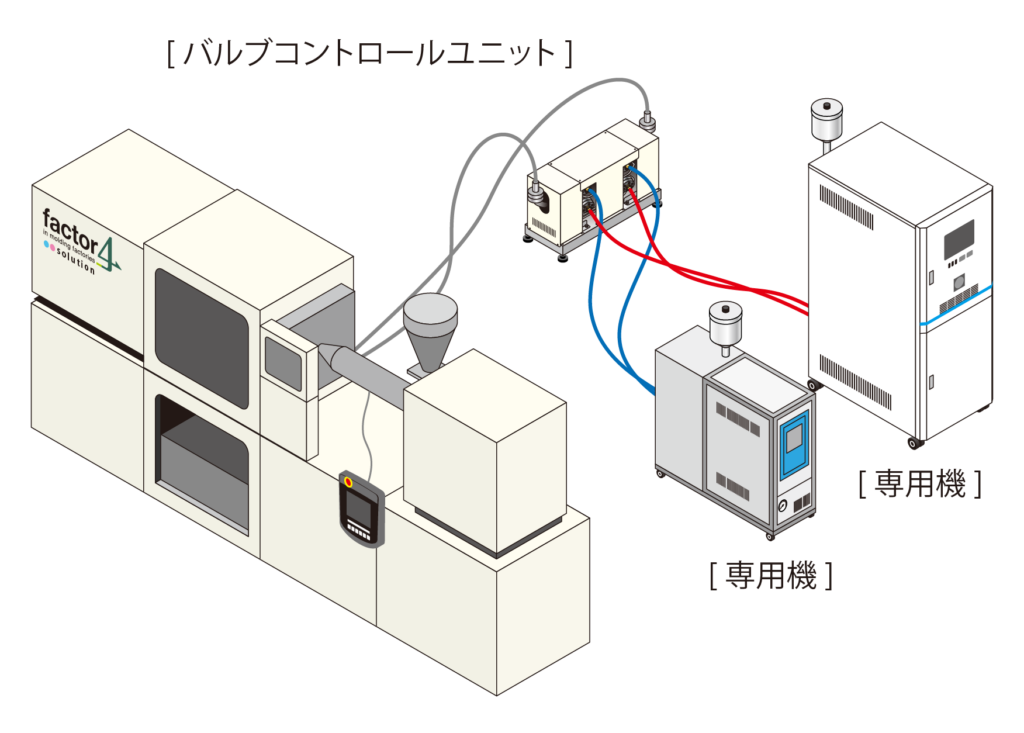

The key to Heat & Cool molding is the repeated rapid heating and cooling, right? But can it be implemented in general-purpose molds as well?

In fact, there is a big difference between general-purpose molds and dedicated molds. We will explain each mold in detail.
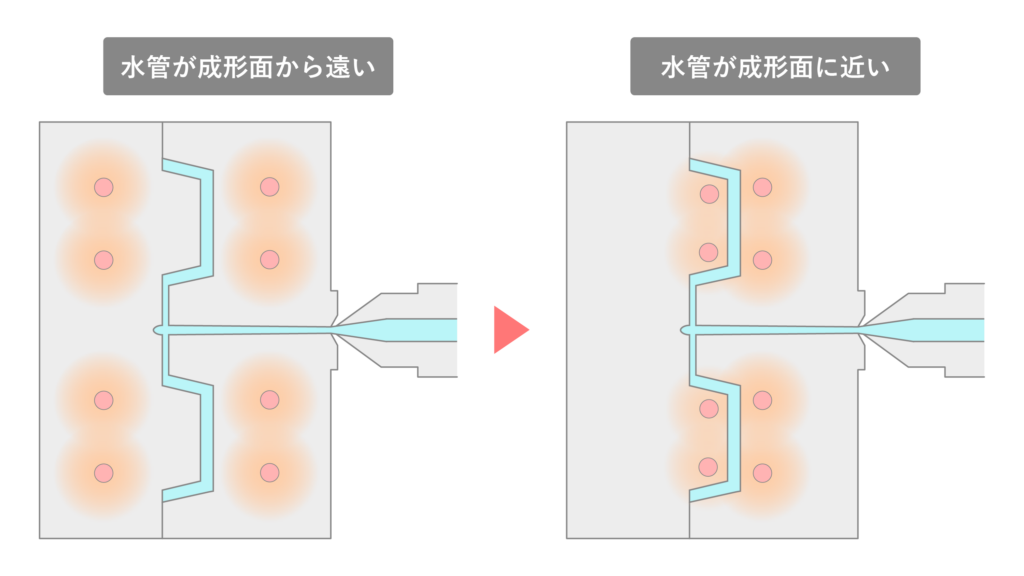
Why we recommend Heat&Cool's dedicated molds
In general-purpose molds, the water pipes inside the mold are often located away from the product surface. This type of structure reduces temperature tracking, making it difficult to fully utilize the rapid heating and cooling effects that are a feature of Heat & Cool molding. As a result, it can be difficult to extend the cycle time or stabilize molding conditions.
On the other hand, dedicated Heat & Cool molds are designed with water pipes placed near the molded product cavity, allowing for efficient heating and cooling of the necessary areas. This significantly improves temperature response, making it possible to effectively suppress appearance defects such as welds and poor transfer. Furthermore, efficient temperature control of the product surface achieves both quality and cycle time.
In other words, "controlling the temperature at the appropriate points" is the key to maximizing the true value of Heat & Cool molding.